Materials
Everything you need is right here but if you want to make any notes, grab some spare paper or a notebook!
A LEARNING RESOURCE FOR SECONDARY YEAR STUDENTS
Everything you need is right here but if you want to make any notes, grab some spare paper or a notebook!

There’s lots of information in this resource – really take your time trying to understand it.
As you go through, think about what you are going to do to raise awareness.

Ask questions – the more you ask, the more you learn!
Research further – there are links to other resources throughout this e-learning that will give you more information, take a look!
If you read anything that upsets or worries you, there will always be someone there to help. You can speak to a member of staff or call the NSPCC helpline on 0808 800 5000. If you think you are in immediate danger, always call 999.

Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) is a human rights violation and child abuse. It happens to millions of girls worldwide and will continue to occur unless we learn about it and come together to take action to prevent it from happening.
This e-learning will help you to start to understand what the practice is, who it affects, and what you can do to help bring it to an end. The word search is made up of a range of topics related to FGM that everyone should know about.

Every child or young person is entitled to human rights, no matter what their background
FGM is a violation of the rights of the child. The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) is an agreement by countries to protect children’s rights. Many countries have signed up to this agreement, including the UK, and have promised to ensure that all children and young people have their basic needs met and reach their potential, whatever their ethnicity, gender, religion, language, abilities or culture. Each right is described in an ‘article’ and there are 54 articles making up the Convention.
Here are some examples of the articles:

Article 1: Every child and young person under the age of 18 has rights

Articles 2, 14 and 31: No matter what your race or language you have the right to enjoy your own culture and use your own language

Article 14: Every child and young person has the right to enjoy and practise their own religion, with their parents’ guidance

Articles 24 and 27: Every child and young person has the right to nutritious food, clean water and a good standard of health care

Article 19: Every child and young person has the right to be treated well and to not be hurt by anyone, this includes the right to be protected from FGM

Articles 18 and 29: Every child and young person has the right to access free education and be given the opportunity to achieve their full potential

Articles 12, 13 and 14: Every child and young person has the right to say how they feel, be listened to and taken seriously

Article 7: Every child and young person has the right to a family who cares for them and keeps them safe

Articles 15 and 31: Every child and young person has the right to relax and play, to attend safe activities such as music, sports, art and meet with friends

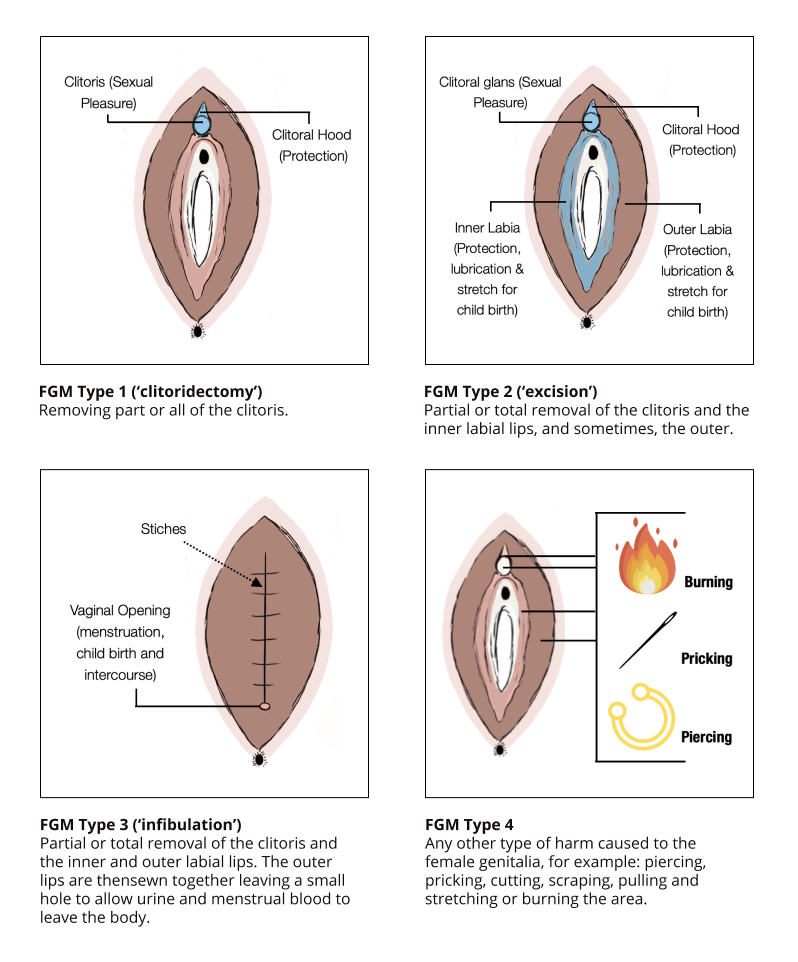
The World Health Organisation, who is responsible for developing guidelines to promote good health and prevent diseases worldwide, defines FGM as: ‘Any procedure that involves harming or removing any part of a girl’s external genitalia’
The female anatomy includes parts inside and outside the body. The parts outside the body have many functions, including protecting the internal parts and should not be removed or harmed. To understand what happens to a girl who has undergone FGM, it is important that you learn about the parts of the external genitalia, so that you understand what happens to a girl who has undergone FGM.
The parts are:


There are four different types of FGM:

Violates a girl’s/woman’s right to be free from violence

Violates a girl’s/woman’s right to make decisions about her own body

Violates a girl’s/woman’s right to health

No one really knows where FGM truly started, and some believe it started in ancient Egypt. FGM now happens all over the world.
There are lots of different terms for FGM around the world, including female genital cutting, female circumcision, ‘cut’ or ‘closed’. What someone calls FGM is dependent on the language they speak. The meaning of some of the names might suggest FGM is a positive practice, however, there are no benefits to it. Below are examples of languages, the names used for FGM and the meaning of the words in some FGM affected countries. You can also see more at the National FGM Centre’s website: https://nationalfgmcentre.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/FGMTerminology-for-Website.pdf
| COUNTRY | LANGUAGE | TERMS | MEANING |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egypt | Arabic | Khitan Khifad Thara |
Circumcision To lower To clean/purify |
| Yemen | Arabic | Al-takmeed U Kwevha |
Compression Elongation of the labia minora |
| Somalia | Somali | Gudiniin Halalys Qodiin |
Circumcision Sanctioned - implies purity stitching/tightening/sewing |
| Singapore | Malay Malay |
Sunat Khitan, perempuan |
Circumcision Female circumcision |
| Peru | Embera |
Curacion | Cure/healing/ treatment |
| Pakistan | Urdu | Khatna | Circumcision |
| Sierra Leone | Soussou Temenee, Mendee Mandingo & Limba |
Sunna Bondo |
Religious tradition Initiation rite into adulthood |
| Ethiopia | Amaharic Harrari |
Megrez Absum |
Circumcision/cutting Name giving ritual |

FGM has no health benefits – it is a form of gender based violence and only causes harm
FGM is not medically required, it can lead to death and there are many health consequences. It is usually practised by people called “cutters” and in some FGM affected countries it is medicalised, which means that it is done by health professionals such as doctors and nurses. Health professionals should not be performing FGM because they are not supposed to cause harm to others. Even if FGM is done under medical conditions, girls can still experience the following health consequences:

Excessive bleeding – this can happen if a blood vessel is cut

Damage to urine hole (urethra) – can cause incontinence and pain when passing urine
Infection – such as HIV, Hepatitis, Septicaemia and Tetanus

Cysts – can develop where the girl has been cut

Pain – cutting the nerve endings and sensitive genital tissue can cause pain

Difficulties in childbirth – for both the mother and the baby

PTSD – mental health problems associated with FGM can include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, nightmares and depression

Flashbacks – flashbacks to the time that FGM took place

Anger towards those or performed the procedure on them and/or those who organised it e.g. family members

There are many activists; women and men worldwide fighting to end FGM. What will you do to help end FGM?
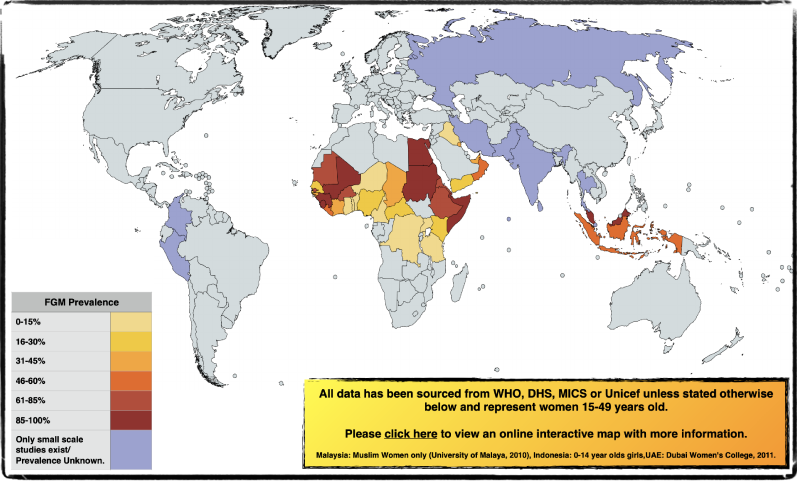
The World Health Organisation states that ‘more than 200 million girls and women alive today have undergone the procedure in 31 countries in Africa, the Middle East and Asia’. Annually, over 4 million girls are at risk of FGM. Because of the increase in population size globally, the number of girls and women subjected to FGM could rise. Below are a handful of FGM affected countries, alongside the prevalence rates and the most common types of FGM practised there.
| COUNTRY | PREVALENCE % | TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| Burkina Faso | 76% | Type 2 |
| Egypt | 87% | Type 1 and 2 |
| Eritrea | 87% | Type 1 and 2 |
| Kenya | 21% | Type 2 |
| Maldives | 13% | Type 1,2 and 3 |
| Mali | 83% | Type 1 and 2 |
| Indonesia | 49% | Type 1 and 2 |
| Yemen | 19% | Type 2 |
| Somalia | 98% | Type 1,2 and 3 |
| Sudan | 87% | Type 1 and 3 |
| Iran | 7% | Type 1 and 2 |
| Nigeria | 19% | Type 2 |
| Gambia | 76% | Type 1 and 2 |
| Ethiopia | 65% | Type 1,2 and 3 |
The movement of people to different parts of the world means that there are girls and women in Europe, North America and elsewhere living with FGM. There are girls and women in the UK living with FGM, but the exact number is difficult to know. Antarctica is the only continent where FGM is not known to occur. You can find out more about prevalence rates across the world using The National FGM Centre’s interactive map on https://nationalfgmcentre.org.uk/world-fgm-prevalence-map/

There are many activists; women and men worldwide fighting to end FGM. What will you do to help end FGM?
FGM can happen for a number of reasons, which differ depending on the affected community. For some affected communities, FGM is important to their culture as it has always been performed over the generations. The practice is supported by both men and women, so should not be considered a topic only for girls and women. The following list gives examples of some of the reasons that some communities give for practising FGM.
Remember, no matter the ‘justification’ given, there are no benefits to FGM, and it causes only harm to girls and women.

Control behaviour – one of the main reasons for practising FGM is to control the behaviour and bodies of girls and women. Those who practise it believe that it may prevent girls and women from experiencing sexual pleasure

Protect a girl’s virginity – to make sure the girl does not have sex before marriage

Cleanliness – some believe that removing parts of the vulva make it cleaner, which is a common misconception as the area is self-cleaning

Money – those who perform FGM e.g. “cutters” and health professionals get paid to perform it, often using the money to support their own families; which has enabled the practice to continue

Beauty – some FGM affected communities believe that a girl or woman with FGM is more beautiful

Marriageability – some men want to marry someone who has FGM as they believe that she has not had sex before marriage, which makes her more honourable

Dowry – in some FGM affected communities, a man has to pay the girl’s family for marrying her. If the girl has had FGM performed, her family could receive more money, as they believe it “confirms” that she’s a virgin

Adulthood – girls undergoing FGM are considered to be a woman, and therefore it is a rite of passage for some communities

The law on its own cannot eradicate FGM. Girls and women must be treated equally, and enjoy the same human rights as boys and men
FGM became illegal in the UK in 1985 when the Female Circumcision Act was enacted. This Act was replaced by the FGM Act 2003. This 2003 Act covers girls and women. According to the Act, anyone found guilty could be fined or imprisoned for up to 14 years or both. The Act states it is an offence to:

Perform FGM in the UK or overseas

Assist someone to perform FGM in the UK or overseas

Assist a girl to perform FGM on herself
In addition to the FGM Act 2003, the Serious Crime Act 2015 also introduced some extra protections for girls and women, including:

FGM Protection Order: a girl, her parents, or anyone else including professionals can go to court to apply for an order which is a document that says what should happen to protect a girl at risk. For example, it could include restricting travel if the judge feels like going abroad could put a girl at risk. It is an offence to breach the order

If a parent/carer fails to protect a girl from FGM happening, they could get up to 6 years imprisonment

Health and social care professionals and teachers in England and Wales are required to report to the police if a girl tells them they have undergone FGM or if they physically see something that makes them believe a girl has undergone the procedure (this is called Mandatory Reporting)

Anonymity for those who have undergone FGM – girls who have to go to court to give evidence against those who have either harmed her or organised the procedure, will never have their identity revealed

Raising awareness about FGM is just one way we can end the practice
Every child and young person has the right to be protected from and live free from all forms of harm. We know that speaking up about FGM can feel scary, but there are specialist services out there, which you can access to help you, like the NSPCC FGM Helpline for example (0800 028 3550) who will be able to support you over the phone. Or, if you or someone you know is worried about FGM, you could also speak to someone you trust like a staff member in school, youth worker, or another adult, who will be able to support you.
Remember, no matter the ‘justification’ given, there are no benefits to FGM, and it causes only harm to girls and women.

National FGM Centre – provides advice, training, lessons and resources for students and professionals www.nationalfgmcentre.org.uk

Daughters of Eve – is a non-profit organisation that raises awareness about FGM and offers support services to people affected by FGM. Visit: www.dofeve.org

FORWARD – offers advice to communities, and training to teachers and students www.forward.org.uk

IKWRO – Provides advice and training to teachers and students www.ikwro.org.uk

Integrate UK – is a youth-led charity that works towards gender and racial equality www.integrateuk.org

Oxford Against Cutting – provides workshops and lessons to staff teams and students www.oxfordagainstcutting.org

Freedom Charity – provides training to staff teams and schools www.freedomcharity.org.uk

The Dahlia Project – provides training on to professionals and communities www.manorgardenscentre.org/dahlia-project